Car Seat Safety Guide
For your child’s safety, it is critical that your child be properly restrained in the appropriate size car safety seat based upon his/her age and weight/ height.
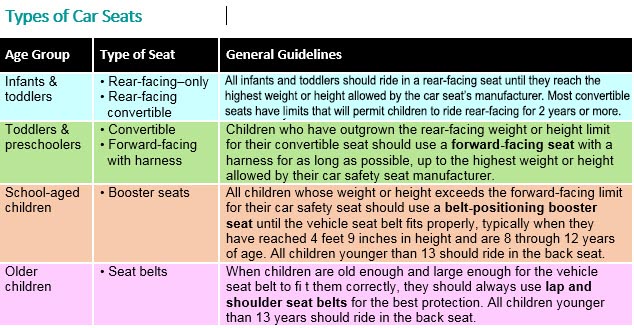
Click HERE for more detailed information.
Medication Dosing Charts
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) Dosing Chart
Give every 4-6 hours as needed but no more than five (5) times per day unless directed your child’s physician.
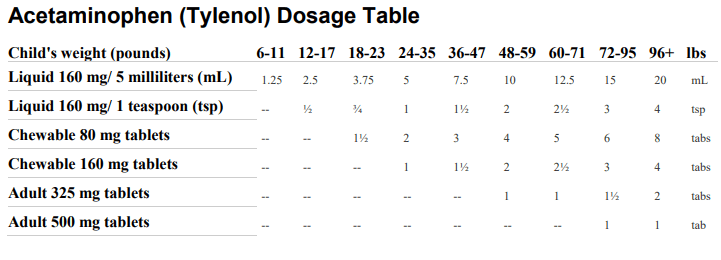
When to Use: Treatment of fever and pain.
Caution: Acetaminophen (Tylenol) can be found in many prescription and over-the-counter medicines. Read the
labels to be sure your child is not getting it from 2 products. If you have questions, call your child’s doctor.
Table Notes:
• Age Limits: Don’t use under 12 weeks of age unless told by child’s doctor. Reason: fever in the first 12 weeks
of life needs to be seen now. If present, your baby needs a medical exam now. Exception: Fever starting within
24 hours of vaccines if child is 8 weeks of age or older. If under 6 years, don’t give products with more than one
ingredient in them (FDA recommendation 2008).
• Dose: Find the child’s weight in the top row of the dose table. Look below the correct weight for the dose
based on the product you have.
• Measure the Dose: Syringes and droppers are better to use than teaspoons. If possible, use the syringe or
dropper that comes with the medicine. If not, you can get a med syringe at a drug store. If you use a teaspoon,
it should be a measuring spoon. Reason: regular spoons are not reliable. Keep in mind 1 level teaspoon equals
5 mL and that ½ teaspoon equals 2.5 mL.
• How Often: Repeat every 4-6 hours as needed. Don’t give more than 5 times a day.
• Adult Dose. 650 mg
• Brand Names: Tylenol, Feverall (suppositories), generic acetaminophen
• Meltaways: Tabs that dissolve come in 80 mg and 160 mg (jr. strength)
• Suppositories: Come in 80, 120, 325 and 650 mg. The rectal dose is the same as the dose given by mouth.
• Extended-Release: Do not use 650 mg oral products in children. Reason: they are every 8-hour extended release.
Author: Barton D. Schmitt, M.D., FAAP
Copyright 1994-2015 Barton D. Schmitt, M.D. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer: This information is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice.
Ibuprofen (Advil/Motrin) Dosing Chart
Give every 6-8 hours as needed but no more than four (4) times per day unless directed your child’s physician.
- AGE LIMIT: Don’t use under 6 months of age unless directed by child’s physician. (Reason: safety not established and doesn’t have FDA approval). Avoid multi-ingredient products in children under 6 years of age. (FDA recommendations 1/2008)
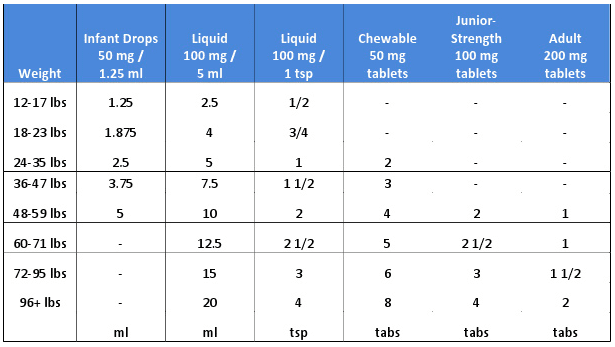
Indications: Treatment of fever and pain.
Table Notes:
- DOSAGE: Determine by finding child’s weight in the top row of the dosage chart.
- MEASURING the DOSAGE: Syringes and droppers are more accurate than teaspoons. If possible, use the syringe or dropper that comes with the medication. If you use a teaspoon, it should be a measuring spoon. Regular spoons are not reliable. Also, remember that 1 level teaspoon equals 5 ml and that ½ teaspoon equals 2.5 ml.
- IBUPROFEN DROPS: Ibuprofen infant drops come with a measuring syringe.
- BRAND NAMES: Motrin, Advil, generic ibuprofen
- ADULT DOSAGE: 400 mg
- FREQUENCY: Repeat every 6-8 hours as needed but no more than 5 times per day.
Disclaimer: This information is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice.
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) Dosing Chart
Give every 6-8 hours as needed but no more than four (4) times per day unless directed your child’s physician.
- AGE LIMITS: For allergies, don’t use under 1 year of age. (Reason: it’s a sedative). For colds, not recommended at any age. (Reason: no proven benefits) Should be avoided if under 4 years old. Avoid multi-ingredient products in children under 6 years of age. (Reason: FDA recommendations 10/2008).
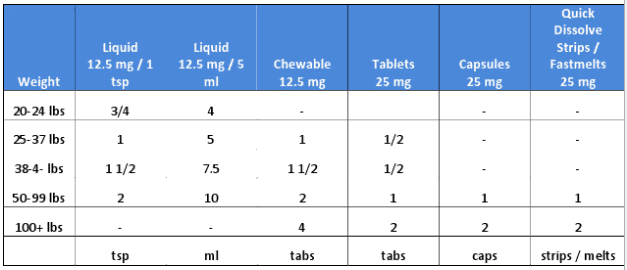
Indications: Treatment of allergic reactions, nasal allergies, hives and itching.
Table Notes:
- DOSAGE: Determine by finding child’s weight in the top row of the dosage chart.
- MEASURING the DOSAGE: Syringes and droppers are more accurate than teaspoons. If possible, use the syringe or dropper that comes with the medication. If you use a teaspoon, it should be a measuring spoon. Regular spoons are not reliable. Also, remember that 1 level teaspoon equals 5 ml and that ½ teaspoon equals 2.5 ml.
- FREQUENCY: Repeat every 6 hours as needed but no more than 4 times per day.
- ADULT DOSAGE: 50 mg
- CHILDREN’S BENADRYL FASTMELTS: Each fastmelt tablet contains the equivalent of 12.5 mg of Diphenhydramine HCL and dosed the same as chewable tablets
Disclaimer: This information is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice.
EMERGENCIES & HOSPITALS
The physicians of Children’s Medical Group have admitting privileges at both the Batson Children’s Hospital at the University of Mississippi Medical Center and Mississippi Baptist Medical Center.
When calling our office about your sick or injured child, please use the term “EMERGENCY” only for conditions requiring immediate treatment, e.g. seizure, uncontrolled bleeding, obstructed or difficulty breathing, poisoning. When possible, please call before coming to the office with an emergency situation to ensure your child receives the attention he/she needs attention upon arrival. We treat minor injuries such as lacerations, burns and sprains in our office. At times, we may need to transfer you to another specialist for care. For example, if a bone is obviously broken, we may refer you to an orthopedist or emergency room. If you believe your child has a life-threatening illness or injury, always CALL 911 immediately.
ILLNESS/INJURY
Below is a list of common illnesses and injuries along with suggestions for the first steps of treatment.
- Burns
Flood the burned area immediately and continuously with ice cold water. Apply no ointments. Call our office for further instructions. - Choking
Do not give children under five years of age nuts, popcorn, hard candy, chewing gum, or whole hotdogs to eat because of the danger of choking. Do not give children under five years of age balloons to play with for the same reason. Toys larger than the child’s mouth are preferable. - Cuts
Cuts that stand open usually require sutures. Please call before coming to the office. The bleeding from cuts should be stopped promptly by direct pressure on the cut using a clean cloth. Usually, cuts in the mouth do not require treatment unless bleeding is not easily controlled or the laceration is large. - Diarrhea
Diarrhea without high fever, mucus or blood in the stool, or prolonged vomiting may be safely treated initially with clear liquids for 6 to 12 hours. As noted previously, Pedialyte is the best fluid for infants. Fruit juice or other sugary drinks may make diarrhea worse. Return to a bland diet within 1 to 2 days as tolerated. Call if problems persist. - Fever
Fever is usually a sign of infection. More important than the height of the fever is the cause of the fever. The initial management of fever is acetaminophen (Tylenol, etc.). Do not give aspirin unless specifically advised by your physician. Ibuprofen may be used in children older than 6 months. For proper dosing, please consult the dosing charts above.- Children who have fever without a known cause, especially if accompanied by persistent vomiting, should be seen by the physician. Please call our office to discuss the child’s condition.
- Infants under 2 months of age with even a low grade fever are of special concern. Young infants with drowsiness, irritability or poor feeding even in the absence of fever need to be examined by a physician.
- Seizures
A small percentage of children will have a tendency to have seizures with a rapid rise in temperature. Seizures with fever are generally brief, lasting 3 to 5 minutes. Do not put objects in the child’s mouth. Lay the child on one side with his head lower than his hips. Apply cold cloths to the head. Sponge the entire body with tepid water. Give nothing by mouth. Call the office immediately. If the child is not breathing or the seizure lasts longer than 5 minutes, CALL 911. - Fractures
If there is an obvious deformity or fracture, it is best to contact an orthopedic surgeon directly or take your child to the Emergency Room. - Head Injuries
In general, if there is no unconsciousness, vomiting, prolonged pain or unusual drowsiness, an examination by your child’s physician is not necessary. You should check with us by phone if there is any question in your mind regarding the seriousness of the injury. Cold compresses may be used for swelling in the absence of worrisome signs. - Insect Stings
Calamine lotion or a hydrocortisone cream may be used for mild itching. Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) (without decongestant) may be given orally if itching or swelling are more prominent. For proper dosing information, please consult the dosing chart HERE. - Vomiting
Vomiting without other symptoms should be treated by giving nothing by mouth for the first 2 to 3 hours, followed by frequent, small amounts of clear liquids as tolerated. In infants, the use of Pedialyte for up to 24 hours is by far the best fluid to maintain hydration. A marked decrease in urine output is a very significant sign of dehydration. Call if vomiting persists or if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as restlessness, excessive drowsiness, or rapid breathing.
POISON CONTROL CENTER
If you believe that your child has a poisoning emergency, call Poison Control at 1-800-222-1222. If the child is unresponsive or not breathing, CALL 911. Medicines, poisons, insecticides, and other household chemicals should be kept out of the reach of children and safely locked away.
SYMPTOM CHECKER
Click HERE to access the healthlychildren.org KidsDoc Symptom checker.
WELLNESS
Caring For Your Child
